Risk of Prostate Cancer: 5 Things You Can Do That Reduce Your Risk
Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Eating a healthy diet is an important way to help prevent prostate cancer. Fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants, which can help protect your cells from damage that can lead to cancer. Fruits and vegetables that are particularly beneficial for prostate cancer prevention include cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli, kale, and cauliflower), tomatoes, citrus fruits, berries, apples, and pears. Cruciferous vegetables contain compounds that can help protect cells from damage that can lead to cancer. Tomatoes are high in lycopene, an antioxidant that can help lower the risk of prostate cancer. Citrus fruits, such as oranges and lemons, are rich in vitamin C, which has been shown to help reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Berries are also high in antioxidants, which can help protect your cells from damage. Apples and pears contain compounds that can help reduce inflammation, which can help protect against cancer. Whole grains are a great source of fiber, which can help keep your digestive system healthy. Eating a wide variety of colorful fruits and vegetables is key, as different colored produce contain different vitamins and minerals that can help protect your body from disease.
Exercise Regularly
Exercising regularly is a great way to help prevent prostate cancer. Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy weight, which in turn can reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Exercise also helps to lower levels of certain hormones in the body, such as testosterone, which has been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Additionally, physical activity can help reduce inflammation in the body, which has also been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Finally, exercise helps to boost the immune system, which can help the body better fight off cancer-causing agents.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health, and can also help reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer. Excess body fat has been linked to higher levels of certain hormones, such as testosterone, which can increase the risk of prostate cancer. Obesity can also lead to increased levels of inflammation in the body, which has been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. Keeping a healthy weight helps to keep hormones and inflammation at healthy levels, which can help protect against prostate cancer.
Meralgia Paresthetica: Sleep Positions and Exercises for Relief
Screening for Prostate Cancer
Talking to your doctor about screening for prostate cancer is an important way to help prevent the disease. Regular screenings can help detect prostate cancer early, when it is most treatable. The type of screening recommended will depend on your age, family history, and other risk factors. For example, all men over the age of 50 should talk to their doctor about screening for prostate cancer, as should those with a family history of the disease.
“The discussion about screening should take place at:
· Age 50 for men who are at average risk of prostate cancer and are expected to live at least 10 more years.
· Age 45 for men at high risk of developing prostate cancer. This includes African Americans and men who have a first-degree relative (father or brother) diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age (younger than age 65).
· Age 40 for men at even higher risk (those with more than one first-degree relative who had prostate cancer at an early age).”
American Cancer Society Recommendations for Prostate Cancer Early Detection
 |
| Photo by Los Muertos Crew |
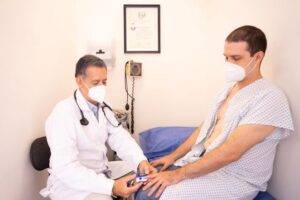
Your doctor may recommend a digital rectal exam, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, or other tests to help detect prostate cancer. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for regular screenings in order to catch any signs of prostate cancer early.
Tips for Back Pain: Your Guide to Causes, Prevention, and Relief
Avoid Red Meat and Processed Meat
Avoiding or limiting consumption of red meat and processed meat is an important way to help prevent prostate cancer. Red meat, pork, and processed meats, such as bacon and sausage, can contain high levels of saturated fat and preservatives, which can increase inflammation in the body and in turn increase the risk of prostate cancer. Studies have also found that men who ate larger amounts of red meat or processed meat had a higher risk of developing prostate cancer than those who ate less. It is recommended to limit consumption of red meat and processed meat, and instead focus on eating lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and plant-based proteins.
Overall, there are many things that men can do to help prevent prostate cancer. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, talking to your doctor about screening for prostate cancer, and avoiding or limiting consumption of red meat and processed meat are all important steps that men can take to reduce their risk. By making these lifestyle changes, men can help reduce their risk of prostate cancer and maintain their overall health.
You may also like to read Lose Weight and Feel Great on a Plant-Based Diet, 5 Ways to Keep Your Heart Healthy for American Heart Health Month, The Top 5 Signs and Symptoms of Endometriosis.
FAQ
Q: What is prostate cancer?
A: Prostate cancer is a malignant growth of cells within the prostate gland, a small walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder in men. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men, particularly in older age groups.
Q: What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
A: Early-stage prostate cancer often has no symptoms. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, frequent urination (especially at night), blood in urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, and pain in the hips, back, or chest.
Q: What are the risk factors for developing prostate cancer?
A: Risk factors for prostate cancer include age (risk increases with age), family history (having a close male relative with prostate cancer increases risk), race (African American men have a higher risk), and certain genetic mutations (BRCA1/2).
Q: How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
A: Prostate cancer is often detected through routine screening tests such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test or a digital rectal exam (DRE). If abnormal results are found, further tests like a biopsy, MRI, or ultrasound may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Q: What are the treatment options for prostate cancer?
A: Treatment options for prostate cancer depend on the stage, aggressiveness, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. Common treatments include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Keywords: Healthy diet, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, cruciferous vegetables, tomatoes, citrus fruits, berries, apples, pears, lycopene, vitamin C, antioxidants, inflammation,Prostate cancer, screening, age, family history, risk factors, average risk, high risk, African Americans,Red meat, Processed meat, Lean proteins, Healthy diet, Fruits, Vegetables, Whole grains, Exercise, Not smoking, Maintaining healthy weight










